🧠 In Today’s World of Gym-Class-Club, Have You Heard of Omega-3?
If you’re even a little bit into a healthy lifestyle, gym routine, or skincare, you’ve probably heard people talk about Omega-3 fatty acids. It’s one of those buzzwords thrown around by doctors, nutritionists, and even influencers. But let’s be honest — between work, workouts, and WhatsApp, most of us don’t really have time to know what Omega-3 actually is, right?
In simple terms, Omega-3 is a type of good fat — the kind that keeps your heart beating fine, your brain sharp, your eyes bright, and your joints flexible. But what exactly makes it “good”? Why can’t we get enough from a regular Indian meal, and why are doctors and gym trainers equally obsessed with it? Let’s decode everything you need to know about Omega-3 fatty acids in the most relatable way.
———
🧬 What is Omega-3?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential polyunsaturated fats (often called good fats) that your body and mind need to function properly. The word essential here is key, because your body can’t make Omega-3s on its own. So, you must get them through your special diet or from supplements like fish oil or algae-based capsules.

👉 Dear vegetarians, don’t worry — there are plenty of plant-based sources too! We’ll explore them in detail below.
———
🔬 The Science Behind It — Types of Omega-3
Everything in the human body is made up of proteins, fats, carbs, and DNA, which are made up of carbon chains. Omega-3 fatty acids have a specific structure: a carbon double bond placed three carbons away from the end of the chain. That’s where the “3” comes from. And there are three main types of Omega-3s you should know about:
- ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid) is found mainly in plant-based foods like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. ALA is essential, but your body can convert only a small portion of it into other useful forms.
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid) is found mostly in fatty or cold-water fish such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel. EPA supports heart health, reduces inflammation, and boosts mood.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) is one you’ve probably heard of in baby milk ads! DHA is vital for brain and eye development, especially in infants and during pregnancy. It’s mainly found in fish and algae.
The body’s ability to convert ALA into EPA and DHA is quite limited (less than 10%), which means vegetarians often miss out on the most beneficial types of Omega-3 unless they consume fortified foods or omega-3 supplements.
———
🥗 Why Regular Indian Food Isn’t Enough
Even if you eat “healthy,” most modern diets, especially Indian food, are low in Omega-3 and high in Omega-6 fats, which is a problem…
- 🌾 Refined oils (sunflower, soybean, corn) dominate our cooking, and they’re rich in Omega-6, which blocks the observation of Omega-3 in your body.
- 🥬 Vegetarian meals, though nutritious, lack DHA and EPA — the forms most useful for your brain and heart.
- 🐟 Fish consumption is often limited, either due to availability, high cost, or concerns about mercury and microplastics.
Even with a healthy diet, your Indian thali may not provide the Omega-3 that much your body needs. That’s why Omega-3 supplements like fish oil or algae oil have become such an “easy-to-have” for people who want guaranteed nutrition without dietary struggles.
———
🐟 Major & Easily Available Sources of Omega-3
Rich Sources (Non-Vegetarian):
- Fatty Fish (Cold Water Fish): Salmon, sardines, tuna, mackerel, herring
- Fish Oil Capsules: Easily available online and provide a concentrated dose of EPA & DHA
- Cod Liver Oil: Classic choice rich in Omega-3 and Vitamin D
Vegetarian & Easily Available Sources:
- Flaxseeds / Flaxseed Oil: There are 2.3g of omega-3 per tablespoon (raw seeds) & 7g per tablespoon (oil).
- Chia Seeds: Super easy to add to smoothies or overnight oats, and there are 17–18g of omega-3 per 100g.
- The Only Nut Rich in Omega-3: Walnuts are a handful daily, keep your heart happy, and there are 2.5g of omega-3 per 100g.
- Soybeans: Great in curries or salads, and there are 100g of omega-3 per 100 g.
- Canola & Mustard Oil: 9–11g per 100ml, so, just switch your cooking oil
- Grass-fed Cow Milk: 30–50mg per 100ml — small, but consistent. You may try Lactogen Milk for babies if fresh cow milk is not available.

👉 Fun tip: Sprinkle chia seeds on curd, mix flaxseed powder in roti dough, or add walnuts to your halwa — small changes, big benefits.
———
👉🏻 Major Benefits of Omega-3
Omega-3s are like the all-rounder player of nutrition, while supporting almost every system in your body.
❤️ 1. For the Heart:
- It reduces triglycerides and bad cholesterol (LDL)
- It improves blood flow & prevents artery blockage
- It helps prevent heart attacks and strokes
🧠 2. For the Brain:
- It enhances memory, focus, and mood
- It reduces depression and anxiety symptoms to improve sleep.
- It lowers the risk of Alzheimer’s and age-related brain issues.
👀 3. For the Eyes:
- DHA supports retina health, improving vision clarity
- Prevents dry eyes and early eye sight issues, especially for those who spend too much screen time, which means we all do.
🦴 4. For Joints:
- It reduces inflammation and stiffness in arthritis
- It improves flexibility — great for gym-goers and the elderly alike
👩🍼 5. For Women’s Health:
- It balances hormones and reduces menstrual pain
- It supports fetal brain and vision development during pregnancy
- It reduces postpartum depression, but always consult your Gyna first!
🌿 6. For Skin & Immunity:
- It gives your skin a healthy glow by locking in moisture
- It strengthens immune function and improves gut health
——–
📏 How Much Omega-3 Should You Take?
| Category | Recommended Daily Intake |
|---|---|
| Children (1–8 years) | 0.7–1 g/day |
| Teens & Adults | 1–1.6 g/day |
| Pregnant/Lactating Women | 1.4–2 g/day |
| Gym-Goers | 1–3 g/day |
| Older Adults | 1–2 g/day |
💡 Aap Ka Bazar Tip: Always consult your doctor before starting any supplement or diet, especially if you have any health issues, pregnancy, or are on medication.
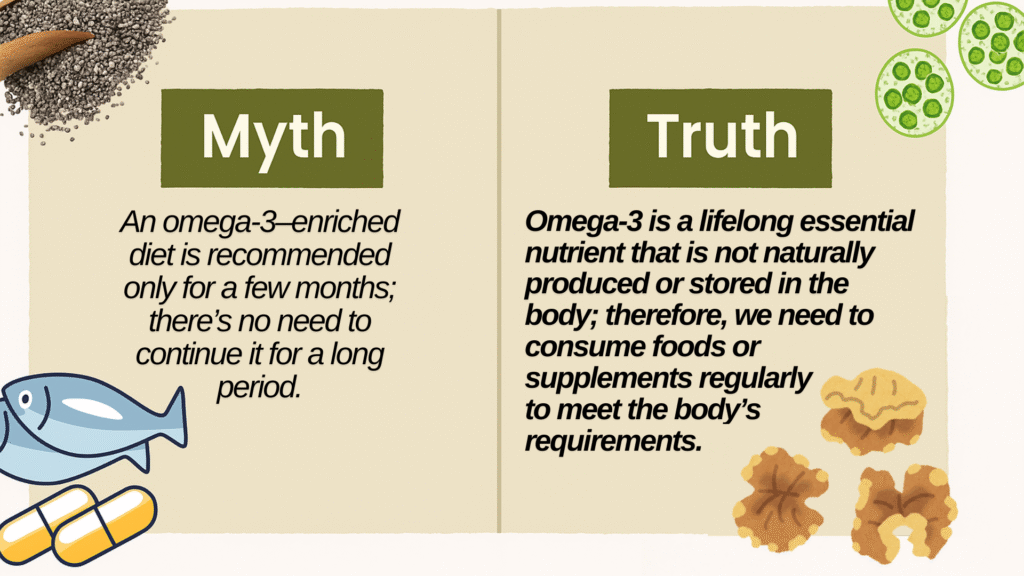
🧩 Common Myths & Facts About Omega-3 Fatty Acids
| ❌ Myth | ✅ Fact |
|---|---|
| Omega-3 comes only from fish. | Vegetarian sources like chia, flax, walnuts, and algae oil also provide Omega-3. |
| Vegetarians can’t take Omega-3. | Algae oil supplements are 100% plant-based and rich in DHA & EPA. |
| Omega-3 causes digestive problems. | In proper dosage, Omega-3 actually improves digestion and gut health. |
| All fats are bad. | Omega-3 is a good fat crucial for heart, brain, and skin health. |
| You don’t need supplements if you eat “healthy.” | Most diets lack DHA & EPA — supplements fill that gap. |
| Omega-3-rich diets are expensive. | Not true! On the Grocery App for Dwarka Sector 19 Delhi, you can get up to 50% off on seeds, walnuts & oils. |
Omega-3 isn’t just another fitness trend; it’s a lifelong nutrient that supports your body from head to toe. Whether you’re a student struggling with focus, a gym enthusiast chasing gains, or a parent caring for your family’s health, Omega-3 plays a silent yet powerful role.
So, make small changes, just switch to mustard oil, snack on walnuts, or take a daily capsule, and your body will thank you in ways you’ll notice slowly but surely.
Remember, this article gathers facts from reliable health resources and nutrition studies, but your doctor knows your body best. Always seek professional advice before starting any supplement routine.
Stay healthy, stay heart-strong, and keep that good fat flowing.